Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

In today’s data-driven world, organizations require robust solutions to manage, store, and analyze massive amounts of data efficiently. The emergence of the lakehouse concept has transformed how businesses handle data, offering a hybrid approach that combines the best features of data lakes and data warehouses. In this guide, we’ll explore what a lakehouse is, how it differs from traditional architectures, and why companies are adopting this innovative model.
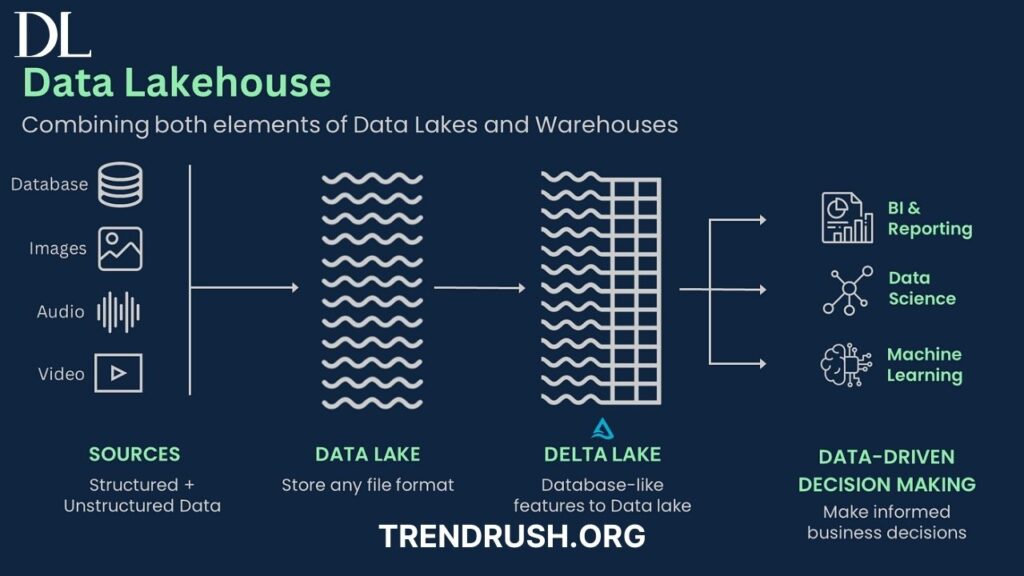
A Data Lakehouse is a modern data architecture that blends the structured capabilities of a data warehouse with the flexibility and scalability of a data lake. It provides a single platform for storing raw and structured data while enabling real-time analytics, governance, and performance optimization.
The lakehouse model eliminates the silos between data lakes and warehouses, offering businesses a unified approach to handling data. It integrates transactional and analytical processing, making it easier to perform business intelligence (BI), machine learning (ML), and AI-driven insights.
A lakehouse offers several features that make it a powerful data management solution:
A lakehouse operates by integrating the best capabilities of data lakes and data warehouses into a unified architecture. Here’s how it works:
By integrating these processes, a lakehouse eliminates the inefficiencies of separate data lakes and data warehouses, making data management more effective and streamlined.
To understand the significance of a lakehouse, it’s essential to compare it with a traditional data warehouse.
| Feature | Lakehouse | Data Warehouse |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | Handles both structured and unstructured data | Primarily structured data |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with cost-effective storage | Limited scalability, expensive storage |
| Performance | Optimized query performance | High performance but costly |
| Flexibility | Supports AI/ML workloads | Designed for BI and SQL queries |
| Cost | More affordable due to open-source technologies | Expensive due to proprietary software |
While data lakes and lakehouses may seem similar, they have distinct differences:
| Feature | Data Lake | Lakehouse |
| Schema | Schema-on-read (flexible but complex) | Schema-on-write (structured and efficient) |
| Data Quality | Poor, requires additional processing | High, includes governance and quality controls |
| Query Performance | Slower due to unstructured data | Faster with built-in indexing and caching |
| Governance | Limited security and governance | Advanced governance and compliance |
The lakehouse addresses the limitations of a traditional data lake by adding governance, reliability, and performance improvements, making it more suitable for enterprise use cases.
To gain a clearer perspective on how these three architectures differ, let’s compare them side by side:
| Feature | Data Lake | Lakehouse | Data Warehouse |
| Data Type | Unstructured, semi-structured, structured | Unstructured, semi-structured, structured | Structured only |
| Schema | Schema-on-read | Schema-on-write | Schema-on-write |
| Data Processing | Batch processing | Supports real-time & batch processing | Optimized for structured data queries |
| Cost | Lower storage costs, high processing costs | Balanced cost-effectiveness | Higher costs due to premium storage & performance |
| Performance | Slow queries, requires additional tools | Faster queries with built-in indexing | Optimized for BI and SQL workloads |
| Governance & Security | Minimal security and governance | Strong governance and security features | Strong governance and security |
The lakehouse serves as a bridge between data lakes and data warehouses, combining the flexibility of a lake with the performance and governance of a warehouse.
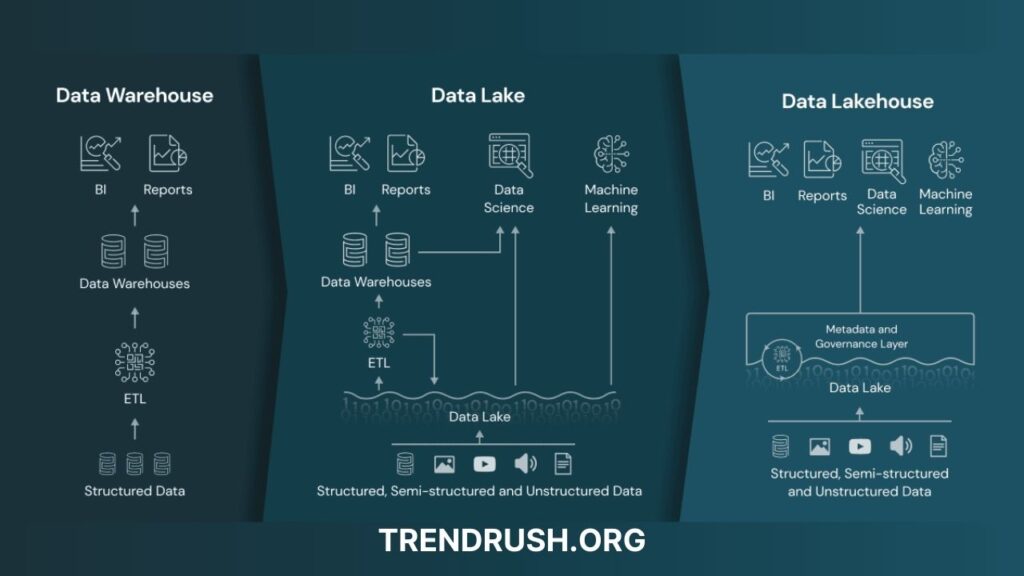
A lakehouse architecture consists of multiple components that ensure efficiency, reliability, and scalability. These components include:
Many tech giants and startups have embraced the data lakehouse model, offering innovative solutions. Some leading companies include:
The Data Lakehouse is revolutionizing data management by combining the best features of data lakes and data warehouses. It provides businesses with a scalable, cost-effective, and high-performance solution for handling vast amounts of data efficiently.
By understanding lakehouse architecture, tools, and real-world applications, organizations can make informed decisions to optimize their data strategy. As more companies adopt this model, the future of data management looks increasingly unified and intelligent.
Are you considering a lakehouse for your business? Explore industry-leading solutions to find the right approach for your needs.